The website is http://www.foodsafetypolicy.com
Information from wikipedia
***
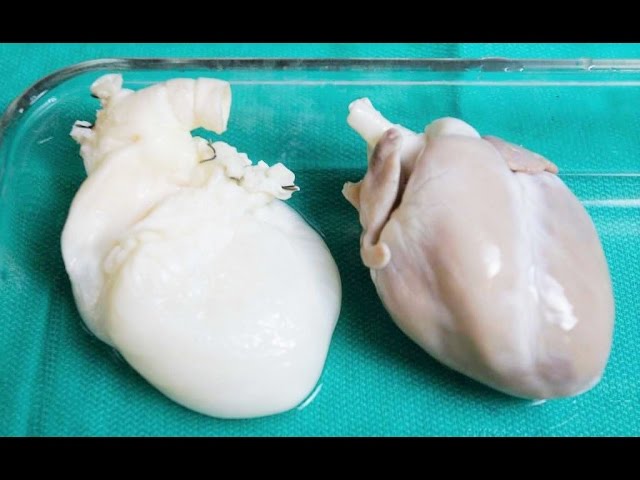
Bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE), commonly known as mad-cow disease, is a fatal neurodegenerative disease in cattle that causes a spongy degeneration in the brain and spinal cord. BSE has a long incubation period, about 30 months to 8 years, usually affecting adult cattle at a peak age onset of four to five years, all breeds being equally susceptible.[1] In the United Kingdom, the country worst affected, more than 180,000 cattle have been infected and 4.4 million slaughtered during the eradication program.
***
Genetically modified foods (or GM foods) are foods derived from genetically modified organisms. Genetically modified organisms have had specific changes introduced into their DNA by genetic engineering techniques. These techniques are much more precise[1] than mutagenesis (mutation breeding) where an organism is exposed to radiation or chemicals to create a non-specific but stable change. Other techniques by which humans modify food organisms include selective breeding; plant breeding, and animal breeding, and somaclonal variation.
***
Food safety is a scientific discipline describing handling, preparation, and storage of food in ways that prevent foodborne illness. This includes a number of routines that should be followed to avoid potentially severe health hazards. Food can transmit disease from person to person as well as serve as a growth medium for bacteria that can cause food poisoning. Debates on genetic food safety include such issues as impact of genetically modified food on health of further generations and genetic pollution of environment, which can destroy natural biological diversity. In developed countries there are intricate standards for food preparation, whereas in lesser developed countries the main issue is simply the availability of adequate safe water, which is usually a critical item. In theory food poisoning is 100% preventable.
***
Nutrition (also called nourishment or aliment) is the provision, to cells and organisms, of the materials necessary (in the form of food) to support life. Many common health problems can be prevented or alleviated with a healthy diet.
The diet of an organism is what it eats, which is largely determined by the perceived palatability of foods. Dietitians are health professionals who specialize in human nutrition, meal planning, economics, and preparation. They are trained to provide safe, evidence-based dietary advice and management to individuals (in health and disease), as well as to institutions. Clinical nutritionists are health professionals who focus more specifically on the role of nutrition in chronic disease, including possible prevention or remediation by addressing nutritional deficiencies before resorting to drugs.
***
Business education involves teaching students the fundamentals, theories, and processes of business. Education in this field occurs at several levels, including secondary education and higher education or university education.
These courses prepare students for an occupation in business or a business-related field, or a teaching career in academia.
At the university level, students have the opportunity to take general business courses, or to seek a specific degree in business studies. Courses offered vary by school, but typically include basic selections such as Accounting, Marketing, Finance, and Operations Management.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y_zLTu9RR9E