http://www.nucleushealth.com/ – This 3D medical animation created by Nucleus Medical Media shows the health risks of smoking tobacco.
ID#: ANH12071
Transcript:
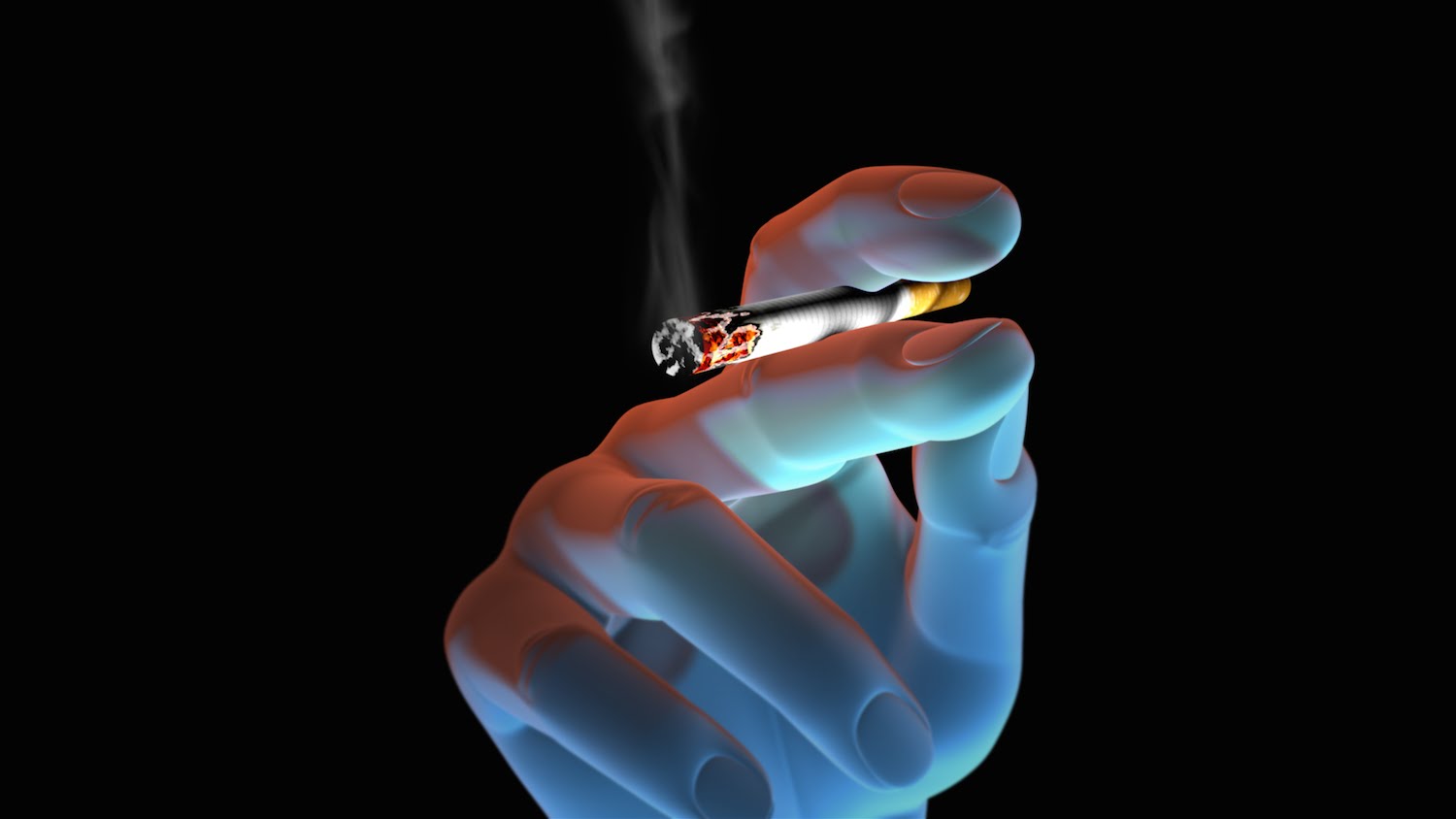
Every time you smoke a cigarette, toxic gases pass into your lungs, then into your bloodstream, where they spread to every organ in your body. A cigarette is made using the tobacco leaf, which contains nicotine and a variety of other compounds. As the tobacco and compounds burn, they release thousands of dangerous chemicals, including over forty known to cause cancer. Cigarette smoke contains the poisonous gases carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxide, as well as trace amounts of cancer-causing radioactive particles. All forms of tobacco are dangerous, including cigars, pipes, and smokeless tobacco, such as chewing tobacco and snuff.
Nicotine is an addictive chemical in tobacco. Smoking causes death. People who smoke typically die at an earlier age than non-smokers. In fact, 1 of every 5 deaths in the United States is linked to cigarette smoking.
If you smoke, your risk for major health problems increases dramatically, including: heart disease, heart attack, stroke, lung cancer, and death from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Smoking causes cardiovascular disease.
When nicotine flows through your adrenal glands, it stimulates the release of epinephrine, a hormone that raises your blood pressure. In addition, nicotine and carbon monoxide can damage the lining of the inner walls in your arteries. Fatty deposits, called plaque, can build up at these injury sites and become large enough to narrow the arteries and severely reduce blood flow, resulting in a condition called atherosclerosis. In coronary artery disease, atherosclerosis narrows the arteries that supply the heart, which reduces the supply of oxygen to your heart muscle, increasing your risk for a heart attack. Smoking also raises your risk for blood clots because it causes platelets in your blood to clump together. Smoking increases your risk for peripheral vascular disease, in which atherosclerotic plaques block the large arteries in your arms and legs. Smoking can also cause an abdominal aortic aneurysm, which is a swelling or weakening of your aorta where it runs through your abdomen.
Smoking damages two main parts of your lungs: your airways, also called bronchial tubes, and small air sacs called alveoli. Cigarette smoke irritates the lining of your bronchial tubes, causing them to swell and make mucus. Cigarette smoke also slows the movement of your cilia, causing some of the smoke and mucus to stay in your lungs. While you are sleeping, some of the cilia recover and start pushing more pollutants and mucus out of your lungs. When you wake up, your body attempts to expel this material by coughing repeatedly, a condition known as smoker's cough. Over time, chronic bronchitis develops as your cilia stop working, your airways become clogged with scars and mucus, and breathing becomes difficult.
Your lungs are now more vulnerable to further disease. Cigarette smoke also damages your alveoli, making it harder for oxygen and carbon dioxide to exchange with your blood. Over time, so little oxygen can reach your blood that you may develop emphysema, a condition in which you must gasp for every breath and wear an oxygen tube under your nose in order to breathe.
Chronic bronchitis and emphysema are collectively called chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD. COPD is a gradual loss of the ability to breathe for which there is no cure.
Cigarette smoke contains at least 40 cancer-causing substances, called carcinogens, including cyanide, formaldehyde, benzene, and ammonia. In your body, healthy cells grow, make new cells, then die. Genetic material inside each cell, called DNA, directs this process. If you smoke, toxic chemicals can damage the DNA in your healthy cells. As a result, your damaged cells create new unhealthy cells, which grow out of control and may spread to other parts of your body. Cigarettes can cause cancer in other parts of your body, such as: in the blood and bone marrow, mouth, larynx, throat, esophagus, stomach, pancreas, kidney, bladder, uterus, and cervix.
Smoking can cause infertility in both men and women. If a woman is pregnant and smokes during pregnancy, she exposes her baby to the cigarette's poisonous chemicals, causing a greater risk of: low birth weight, miscarriage, preterm delivery, stillbirth, infant death, and sudden infant death syndrome. Smoking is also dangerous if a mother is breastfeeding. Nicotine passes to the baby through breast milk, and can cause restlessness, rapid heartbeat, vomiting, interrupted sleep, or diarrhea.
Other health effects of smoking include: low bone density and increased risk for hip fracture among women; gum disease, often leading to tooth loss and surgery; immune system dysfunction and delayed wound healing; and sexual impotence in men.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gwuwrRK-I2Y