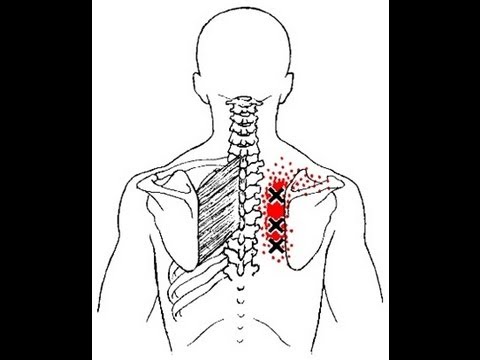
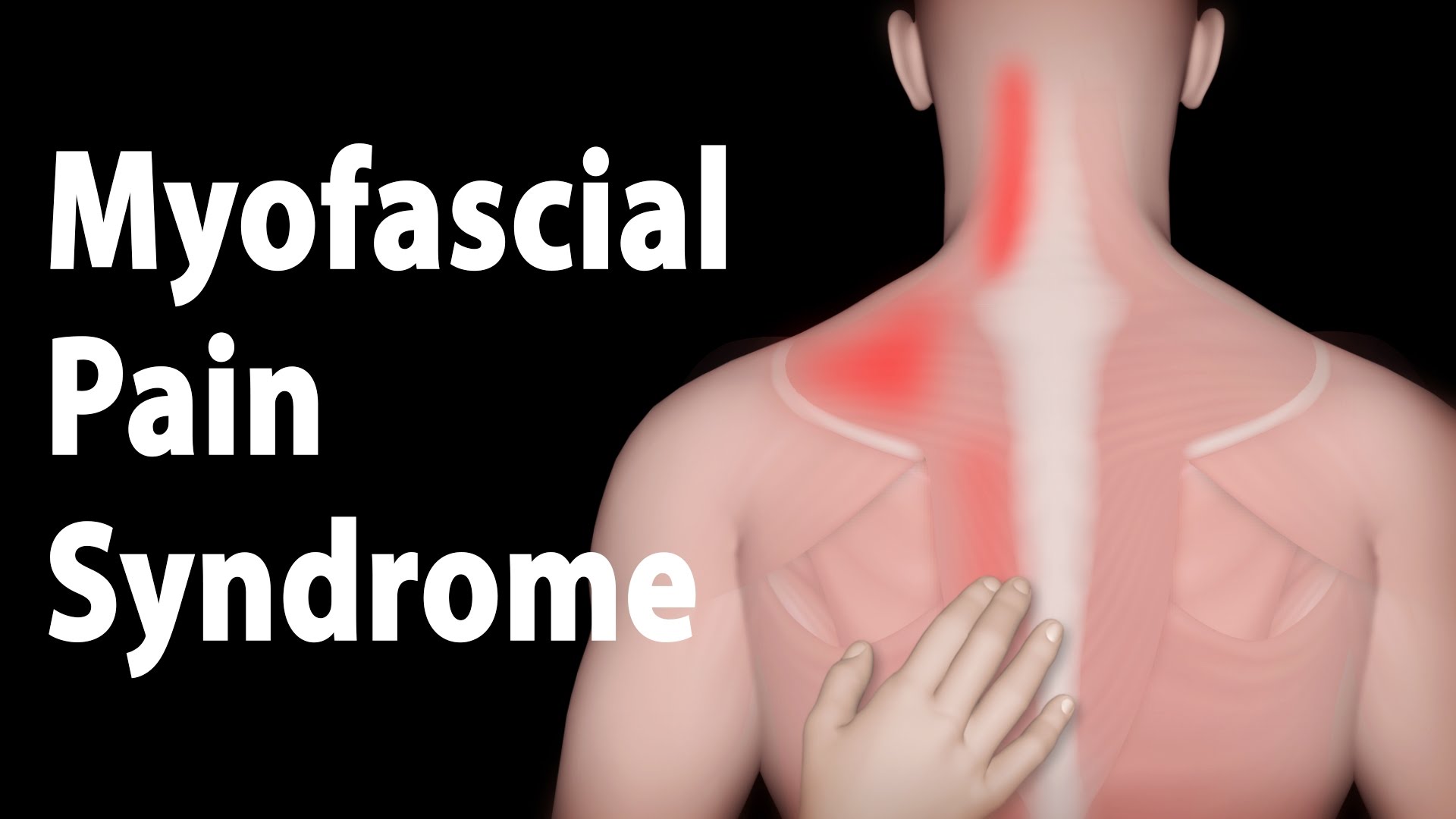
See http://www.gustrength.com/muscles:rhomboid-muscles-location-actions-trigger-points for full article. This video presentation covers briefly the location, origin, insertion, and actions of the rhomboid muscles (major and minor), their trigger points, and referred pain patterns. For a complete overview, related trigger points, with self-treatment guidelines for self myofascial release of sternocleidomastoid trigger points see: http://www.gustrength.com/muscles:rhomboid-muscles-location-actions-trigger-points
GUS Trigger Point Playlist:
GUS Site Trigger Point Category:
http://www.gustrength.com/trigger-points
More Pain Between Shoulder Blades/Interscapular Pain:
http://www.gustrength.com/pain-between-shoulder-blades
For information on self-treatment of trigger points at home see:
http://amzn.to/2kx83qY *
This video uses text and images to describe the rhomboid major and minor muscles, collectively referred to as the "rhomboids."
All images are public domain unless otherwise noted. Unless otherwise noted, images are used under license. Images by LifeART (and/or) MediClip image copyright 2010. Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.- Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. All rights reserved. Images not for reuse.
barbell shrug and bench press images are by http://everkinetic.com/
archery image by Casito via http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Archery_competition.jpg
bad computer posture image by Skoivuma via http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Bad_posture.jpg
BodyParts3D Anatomography images via http://lifesciencedb.jp/bp3d/?lng=en
As noted, the song "Things Ain't Perfect" by Stephen Burns, is used under permission of the composer.
This video is provided by Ground Up Strength for information purposes only and should not take the place of professional medical advice. Although we have done our utmost to provide accurate and safe information, we are not medical professionals and the information in this video should not be taken as professional medical advice, or any other kind of medical advice.
* affiliate link