Assists the searcher in analyzing and evaluating websites in Searcher In Charge Health Information #5. This is the second of three videos that focus on analyzing websites. In the series of Searcher in Charge: Health Information videos, the individual learns how to find and analyze health information needed in their daily life and for consultation with their health care provider. Search techniques, quality health information sources and ways to analyze information and websites, are provided throughout the series of videos so individuals learn to find and review quality health information.
Tag: lung
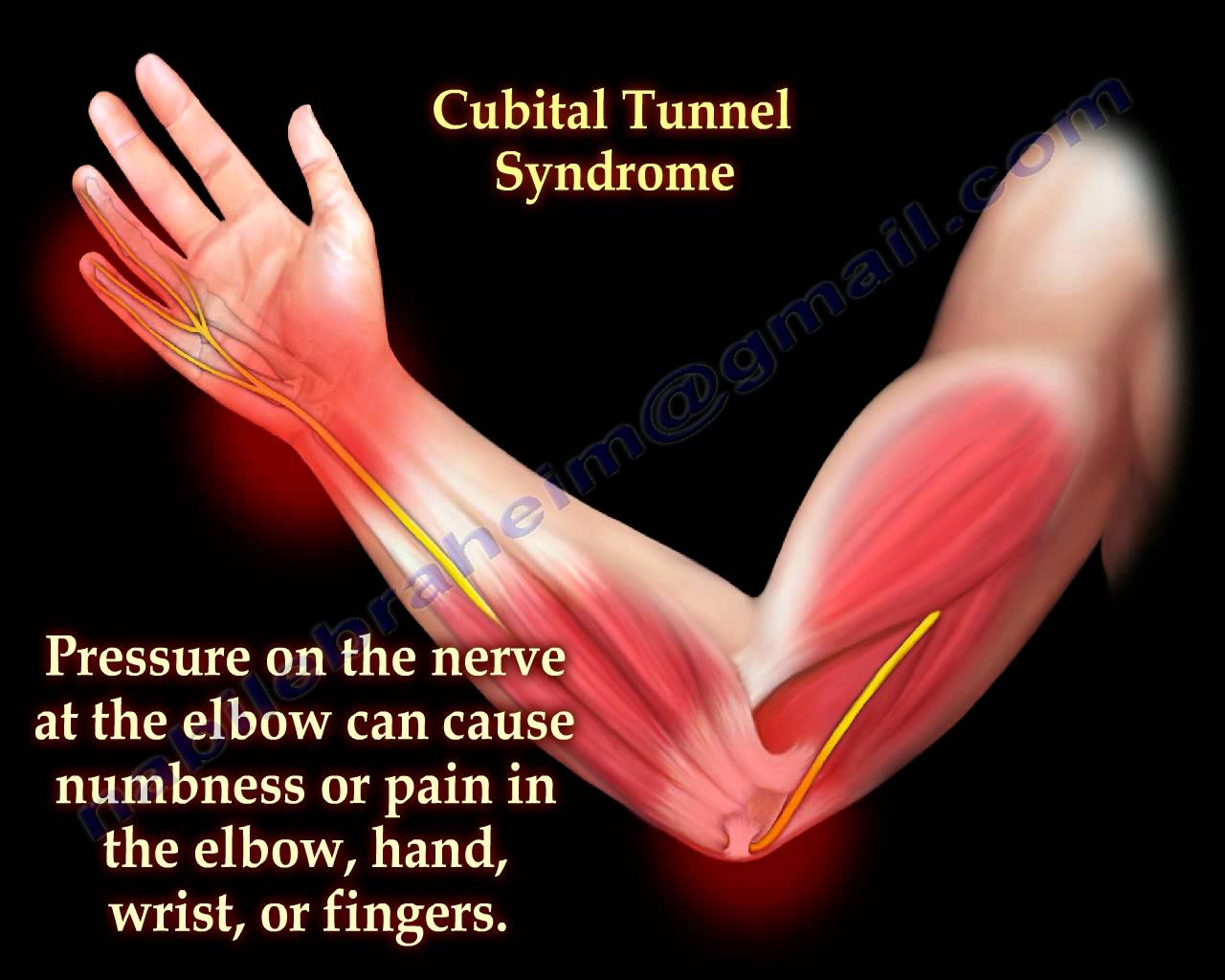
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Ulnar Nerve Entrapment – Everything You Need To Know – Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Dr. Ebraheim’s educational animated video describes the condition of cubital tunnel syndrome and ulnar nerve entrapment , where the ulnar nerve can become pinched in different locations and due to different reasons, such as: thorasic outlet syndrome, Cubital Tunnel Syndrome, Ulnar Tunnel Syndrome(guyon canal).
Causes of ulnar nerve entrapement around the cubital tunnel: Arcade of Struthers, Medial intermuscular septum, Osborne’s Fascia, Cubitus Valgus: a deformity in which the elbow is turned outward, entrapement can also occur due to a spur on the medial epicondyle.
The symptoms of this condition are worsened by preforming activities that require bending the elbow.
Keeping the elbow extended, especially during the night will often relieve the pressure on the ulnar nerve.
Symptoms: the patient will describe symptoms of pain and numbness in the elbow as well as tingling in the ring and little figure.
More severe Symptoms include:
– Weak or clumsy hand.
– Weakness affecting the ring and little fingers.
– Muscle wasting.
– Claw hand deformity if compression below the elbow.
Differential Diagnosis:
– Pain could be due to injury of the cervical spine C8 nerve root.
– Thorasic outlet syndrome: entrapment area between the rib cage and collar bone.
– Pancost tumor: apical lung tumor.
Clinical examination should include:
– Check for Tinnel’s Sign
– Elbow flexion test
– Check for Frement’s sign
Treatment:
– Conservative: NSAIDs, night spling, elbow pad, therapy, injection.
– Surgery: release the nerve with or without transposition.
This condition carry bad prognosis if there is intrinsic muscle atrophy.
Complication of surgery is injury to the medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve.
Neurolysis is not helpful.